Layer masking
A layer mask is used to reveal a portion of a layer while the rest of the layer remains hidden. This means that you can use a mask layer to 'delete' areas of a layer that you don't want.
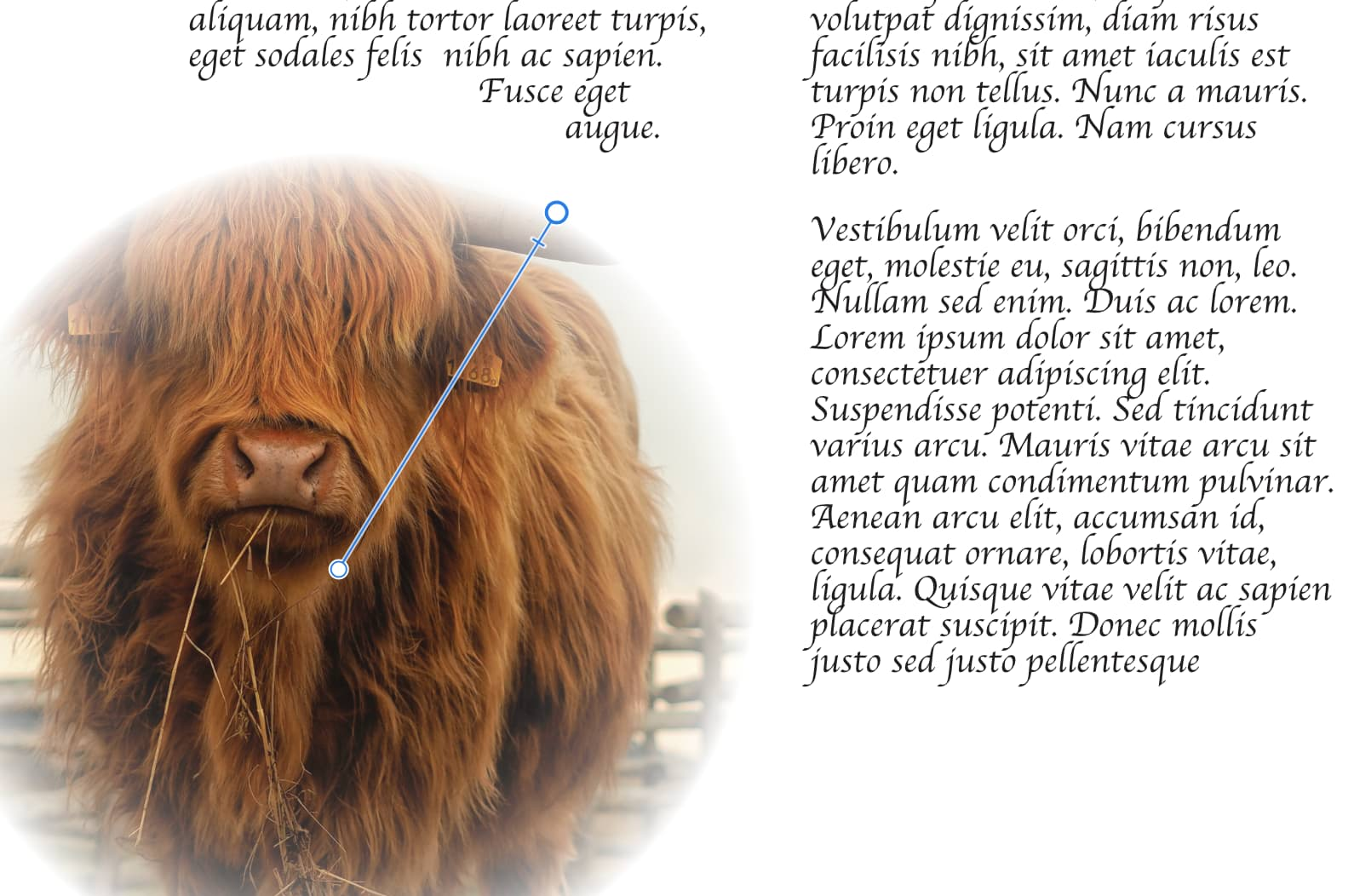
A layer mask is used to reveal a portion of a layer while the rest of the layer remains hidden. This means that you can use a mask layer to 'delete' areas of a layer that you don't want.

Masking can be applied at any level in the Layers panel—as an independent mask layer, applied to a specific layer (or child layer), to groups, or to individual objects. This is governed by the mask layer's positioning in the layer stack.
Masks can be freely edited and moved, and affect any object below them within the same parent layer. They can also be clipped to individual objects so that only that object is affected.
Once a mask layer is created, you can apply different levels of grayscale or opacity to the mask layer—apply White (or 100% Opacity) to reveal; apply Black (or 0% Opacity) to conceal; apply intermediate grayscale levels for partial masking. Try drawing a gradient (with Fill Tool) across a mask layer and assign different grayscale levels or opacity to end stops to experiment.
The thumbnail of the target object changes to indicate that a mask and crop have been applied.
The mask of the object is applied in a "crop to top object" operation.