Layer clipping
Clipping involves positioning one object inside another. The path of the parent object becomes the new boundaries for the child object. Any areas of the child object which lie outside the parent object's path are masked (hidden).
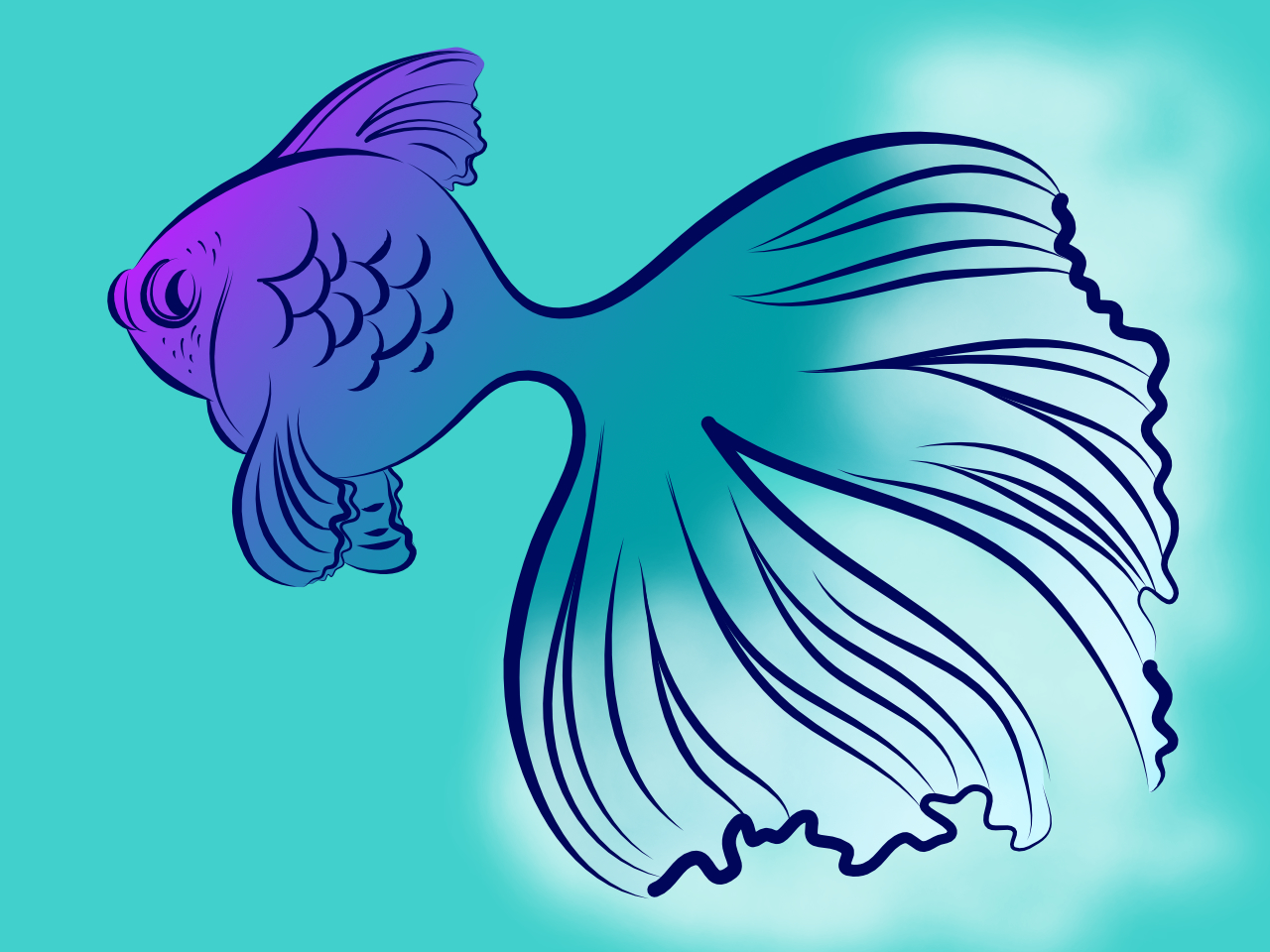
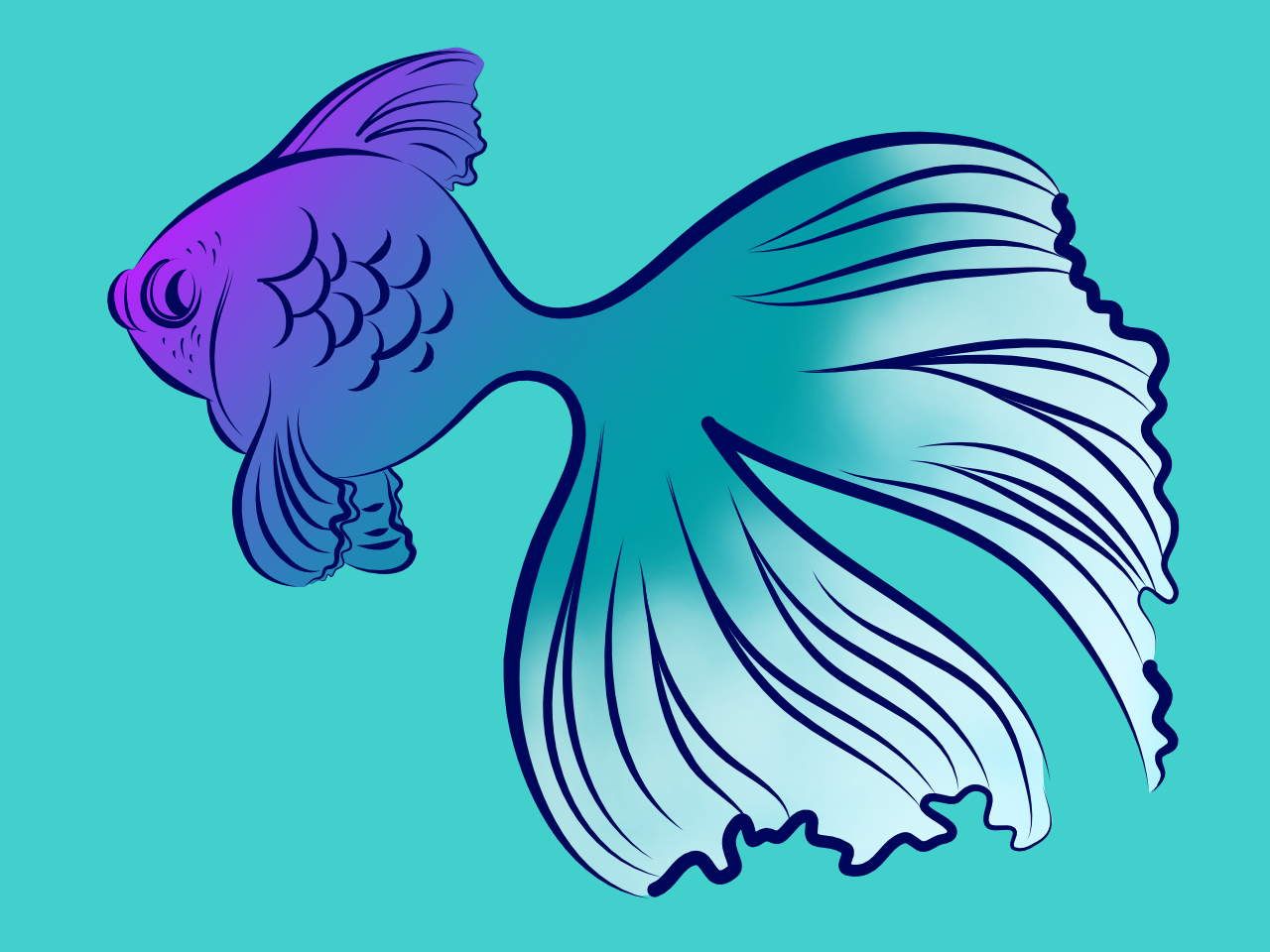


Clipping involves positioning one object inside another. The path of the parent object becomes the new boundaries for the child object. Any areas of the child object which lie outside the parent object's path are masked (hidden).



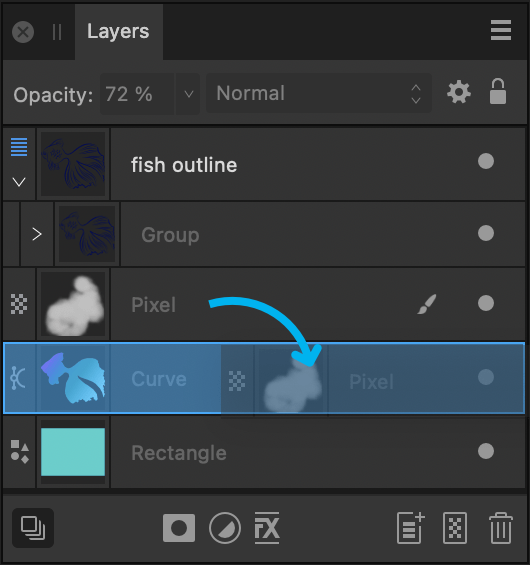
Any object can act as a parent or child in clipping relationships. Both vector objects and pixel layer content can be either clipped or clipping objects. In Affinity Designer, it is popular to clip pixel brush textures to a vector object's outline (see example above).
When scaling a parent object, child (clipped) objects scale to maintain the correct aspect ratio. Scaling a clipped object has no effect on the parent object. A clipped object can be edited independently from its parent, e.g. adjusting color, opacity, and/or blend mode.
The clipped object is nested within the clipping object in the Layers panel. The clipped object has become a child of the clipping object.
Do one of the following: