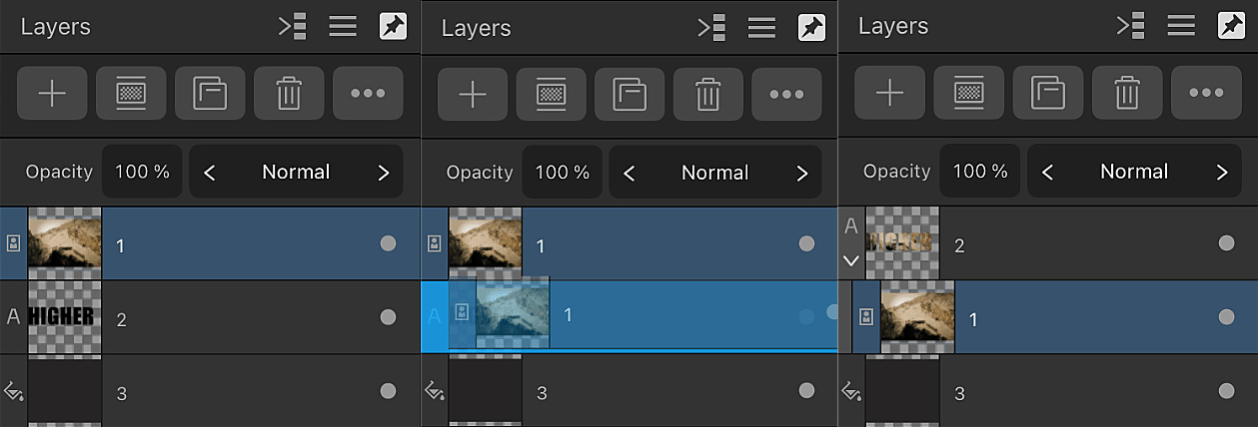
Clipping
Clipping involves positioning one layer inside another, creating a parent-child layer relationship. The path of the parent layer becomes the new boundaries for the child layer. Any areas of the child layer which lie outside the parent layer's path are masked (hidden).
Clipping can also be used to confine an adjustment, filter or mask to a single layer or layer group.